‘Hopes for change to US citizenship-based regime still alive, campaigners say’
By: Helen Burggraf | 17 Nov 2017
Spokespeople for organisations that have been urging US lawmakers, on behalf of expatriate Americans, to legislate for a change to a “residence-based” tax regime said today that the possibility of such a change is still alive, even if it hasn’t yet been spelled out in the latest tax reform plan to be under discussion in Washington.
Their comments came the day after the US House of Representatives passed a tax reform bill that some said was “the most sweeping tax overhaul in three decades, as President Trump moved to leave his mark on the way America does business. The approval came in spite of the objections of the Democratic members of the House and 13 Republicans, and sees the focus now shift to the Senate, which also must approve the legislation for it to become law.
Marylouise Serrato, executive director of the American Citizens Abroad, said today that although residence-based taxation (RBT) isn’t currently mentioned in the bill that was approved yesterday, “there is still movement on RBT, and [still] time for its inclusion” in the final draft. The matter, for example, could also be brought up later on, including during debate on the Senate floor.
“ACA remains hopeful, and we are busy working offices in the Senate, Joint Committee on Taxation (JCT), etc., where we have interested parties,” she added.
Citizenship-based taxation
As reported, the ACA and other organisations representing expatriate Americans have been campaigning hard over the last few months in an effort to draw US lawmakers’ attention to what they say is the dysfunctional way Americans are taxed on the basis of their citizenship, rather than on the basis of where they live, as is the case in all but one other country in the world, the other being Eritrea.
The ACA and Republicans Overseas have been leading the charge, with such other expat American organisations as the Democrats Abroad, Americans for Tax Reform and the Heritage Foundation having also been rallying their members to get US lawmakers to end the US’s citizenship-based regime.
Earlier this year the Republicans Overseas launched a drive to get 6,400 signaturesonto an online petition calling for an end to citizenship-based taxation, while the Democrats Abroad, on 15 June, the day expats tax forms are due by the IRS, staged a “tax storm”, when expats were urged to “join Democrats around the world [in picking up your phone] to ask your representatives and senators for their support for residency-based taxation”.
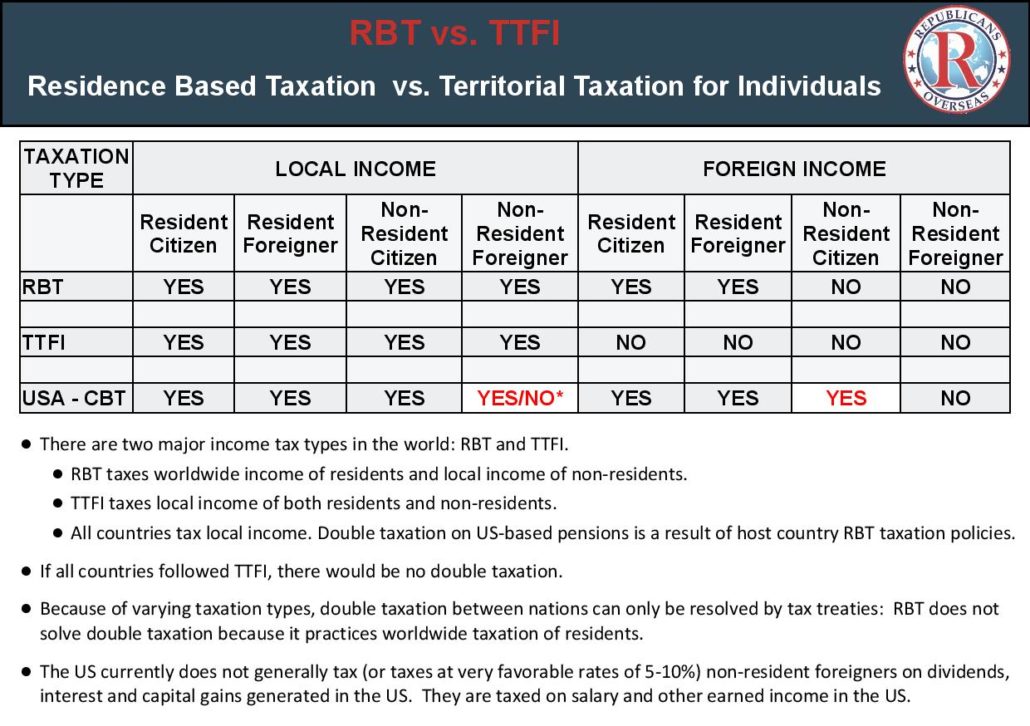
Not all the expat American lobbying groups agree on the exact format the replacement tax regime should take, however, with the Republicans Overseas lobbying in favour of what it calls a “territorial taxation for individuals” regime, or TTFI.
Republican National Committee member Solomon Yue, who is also chairman of the Republicans Overseas, explained recently that although the JCT may make use of some of the research the lobbying groups have conducted in the course of their campaigns, “ultimately it will have to produce its own [formula], according to their procedures”.
The debate over whether the US should, and possibly will, move from a citizenship-based tax regime to one that is based on residency comes as expatriate Americans continue to renounce their citizenships in record numbers, driven by the hassle and expense of having to file returns and be liable for paying taxes in two countries instead of just one. Earlier this month, Bloomberg reported that, based on the most recent data from the Treasury Department, renunciations in 2017 are on track to top 2016’s record number of 5,411, which was itself a 26% jump from 2015.
The Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act, signed into law by president Obama in 2010, is widely credited with sending many expats rushing for the exits, by making the business of being an expatriate American increasingly difficult and expensive, as it requires foreign financial institutions to report to the US tax authorities on any accounts they have that are held by American citizens. Critics call it “the enforcement tool of the US practice of citizenship-based taxation”, but because it has made it difficult for Americans living outside of the US to get bank accounts, mortgages, or otherwise engage in the financial services industries in the countries in which they now reside.
http://www.internationalinvestment.net/products/tax/hopes-change-us-citizenship-based-regime/